前言
GAMES101作业系列为GAMES101作业记录(包含作业1-8),文章中会解释作业内容并附上代码,同时对代码框架进行简要说明。
已完成的代码可在我的GitHubGAMES101作业代码仓库获取。
GAMES101课程相关基础知识可参看本博客GAMES101知识梳理系列。
本文不含提高部分的微表面模型
作业描述
本次实验作业在作业6的基础上实现完整的Path Tracing算法。
主要工作如下:
- 函数迁移:
- Triangle::getIntersection in Triangle.hpp: 将你的光线-三角形相交函数粘贴到此处,请直接将上次实验中实现的内容粘贴在此。
- IntersectP(const Ray& ray, const Vector3f& invDir,const std::array<int, 3>& dirIsNeg) in the Bounds3.hpp: 这个函数的作用是判断包围盒 BoundingBox 与光线是否相交,请直接将上次实验中实现的内容粘贴在此处,并且注意检查 t_enter = t_exit 的时候的判断是否正确。
- getIntersection(BVHBuildNode* node, const Ray ray)in BVH.cpp: BVH查找过程,请直接将上次实验中实现的内容粘贴在此处.
- castRay(const Ray ray, int depth)in Scene.cpp中实现Path Tracing算法
完成作业
函数迁移
复制作业6中的相应函数即可。
请注意,Bounds3::IntersectP函数中进出包围盒时间判断条件有所修改,此前作业中使用的是(tEnter < tExit && tExit > 0),但是在本次作业中会导致天花板和墙壁变黑,因为本次作业中cornell box模型的墙壁和箱子某些三角形是平行于坐标平面的,会出现包围盒厚度为0的情况,此时如果再以tEnter < tExit为条件判断,会错过很多三角形相交。因此需将条件改为(tEnter <= tExit && tExit > 0)
Triangle::getIntersection in Triangle.hpp
// in Triangle.hpp
inline Intersection Triangle::getIntersection(Ray ray)
{
Intersection inter;
if (dotProduct(ray.direction, normal) > 0)
return inter;
double u, v, t_tmp = 0;
Vector3f pvec = crossProduct(ray.direction, e2);
double det = dotProduct(e1, pvec);
if (fabs(det) < EPSILON)
return inter;
double det_inv = 1. / det;
Vector3f tvec = ray.origin - v0;
u = dotProduct(tvec, pvec) * det_inv;
if (u < 0 || u > 1)
return inter;
Vector3f qvec = crossProduct(tvec, e1);
v = dotProduct(ray.direction, qvec) * det_inv;
if (v < 0 || u + v > 1)
return inter;
t_tmp = dotProduct(e2, qvec) * det_inv;
// TODO find ray triangle intersection
inter.coords = ray(t_tmp);//将相交时间t_tmp传给Ray的函数调用运算符,算得交点
inter.distance = t_tmp;
inter.happened = true;
inter.m = this->m;
inter.normal = this->normal;
inter.obj = this;
return inter;
}// in Bounds3.hpp
inline bool Bounds3::IntersectP(const Ray& ray, const Vector3f& invDir,
const std::array<int, 3>& dirIsNeg) const
{
// invDir: ray direction(x,y,z), invDir=(1.0/x,1.0/y,1.0/z), use this because Multiply is faster that Division
// dirIsNeg: ray direction(x,y,z), dirIsNeg=[int(x>0),int(y>0),int(z>0)], use this to simplify your logic
// TODO test if ray bound intersects
Vector3f tMin = (this->pMin - ray.origin) * invDir;
Vector3f tMax = (this->pMax - ray.origin) * invDir;
if(dirIsNeg[0])
std::swap(tMin.x, tMax.x);
if(dirIsNeg[1])
std::swap(tMin.y, tMax.y);
if(dirIsNeg[2])
std::swap(tMin.z, tMax.z);
float tEnter, tExit;
tEnter = std::max(tMin.x, std::max(tMin.y, tMin.z));
tExit = std::min(tMax.x, std::min(tMax.y, tMax.z));
if(tEnter <= tExit && tExit >= 0)
return true;
return false;
}// in BVH.cpp
Intersection BVHAccel::getIntersection(BVHBuildNode* node, const Ray& ray) const
{
// TODO Traverse the BVH to find intersection
Intersection inter, interL, interR;
std::array<int, 3> dirIsNeg;
dirIsNeg[0] = (int)(ray.direction.x < 0);
dirIsNeg[1] = (int)(ray.direction.y < 0);
dirIsNeg[2] = (int)(ray.direction.z < 0);
// 光线与当前包围盒没有交点
if(!node->bounds.IntersectP(ray, ray.direction_inv, dirIsNeg))
return inter;
// 光线与当前包围盒有交点且包围盒是叶子节点
else if(node->left == nullptr && node->right == nullptr){
inter = node->object->getIntersection(ray);
return inter;
}
// 光线与包围盒有交点且包围盒是中间节点
else{
interL = getIntersection(node->left, ray);
interR = getIntersection(node->right, ray);
return interL.distance < interR.distance ? interL : interR;
}
}函数实现
Path Tracing伪代码
shade (p, wo)
sampleLight ( inter , pdf_light )
Get x, ws , NN , emit from inter
Shoot a ray from p to x
If the ray is not blocked in the middle
L_dir = emit * eval (wo , ws , N) * dot (ws , N) * dot (ws , NN) / |x-p|^2 / pdf_light
L_indir = 0.0
Test Russian Roulette with probability RussianRoulette
wi = sample (wo , N)
Trace a ray r(p, wi)
If ray r hit a non - emitting object at q
L_indir = shade (q, wi) * eval (wo , wi , N) * dot (wi , N) / pdf (wo , wi , N) / RussianRoulette
Return L_dir + L_indircastRay
// in Scene.cpp
Vector3f Scene::castRay(const Ray &ray, int depth) const
{
// TO DO Implement Path Tracing Algorithm here
// 直接与间接光照
Vector3f L_dir(0, 0, 0);
Vector3f L_indir(0, 0, 0);
// 与BVH求交
Intersection interObj = intersect(ray);
// 无交点
if(!interObj.happened)
return Vector3f();
// 打到光源 若交点材质发光,则是光源,返回光源颜色
if(interObj.m->hasEmission())
return interObj.m->getEmission();
// 直接光照
Intersection interLight;
float pdfLight;
sampleLight(interLight, pdfLight);
Vector3f p2x = interLight.coords - interObj.coords;
Vector3f p2xDir = p2x.normalized();
float p2xPow = p2x.x * p2x.x + p2x.y * p2x.y + p2x.z * p2x.z;//|x-p|^2
Ray p2xRay(interObj.coords, p2xDir);//ray from p to x
Intersection inter = intersect(p2xRay);
//float比较 当交点p与光源采样点x的求交距离和实际距离之差
if(inter.distance - p2x.norm() > -EPSILON){
L_dir = interLight.emit * interObj.m->eval(ray.direction, p2xDir, interObj.normal)
* dotProduct(p2xDir, interObj.normal) * dotProduct(-p2xDir, interLight.normal)
/ p2xPow / pdfLight;
}
// 间接光照
if(get_random_float() < RussianRoulette){
Vector3f p2nextpDir = interObj.m->sample(ray.direction, interObj.normal).normalized();
Ray p2nextpRay(interObj.coords, p2nextpDir);
Intersection interNextP = intersect(p2nextpRay);
if(interNextP.happened && !interNextP.m->hasEmission()){
float pdf = interNextP.m->pdf(ray.direction, p2nextpDir, interObj.normal);
L_indir = castRay(p2nextpRay, depth + 1)
* interObj.m->eval(ray.direction, p2nextpDir, interObj.normal)
* dotProduct(p2nextpDir, interObj.normal) / pdf / RussianRoulette;
}
}
return L_dir + L_indir;
}castRay函数中完成的是对每条光线的计算,多少SPP就对每个像素调用多少次。
若无交点,则返回空Vector3f;若直接打到光源,则返回光源颜色。
之后才是真正计算直接与间接光照。
- 直接光照部分:
(sampleLight函数中将计算结果赋值给interLight, pdfLight,因此这两者可以不用初始化)
计算采用对光源进行采样积分的方法。如伪代码中所述,需要判断光源与物体之间有无遮挡,这里采用的方法是生成一条由物体上的点射向光源采样点的光线,对该光线进行求交,如果求交得到的距离与物体上的点到光源采样点的距离相等,则中间无遮挡。
遮挡判断在实际实现时,是两距离之差小于一定值即为相等,这是因为float型比较问题。代码中写作
inter.distance - p2x.norm() > -EPSILON这种写法初看可能会觉得有点奇怪。这么写的原因是,inter.distance是光线求交算得的距离,p2x.norm()是直接计算出的两点距离,而inter.distance是从物体指向光源的光线,因此只可能<=p2x.norm(),绝不可能大于p2x.norm(),因为其可能存在的最远交点就是光源采样点。
当满足上述条件后,即使用对光源采样的蒙特卡洛积分方法计算该点直接光照。
- 间接光照部分:
为了防止追踪过程无限递归,引入俄罗斯轮盘赌方法。若由轮盘赌结果光线存活,则有采样函数生成,对该光线进行追踪,若其与不发光物体相交则用对蒙特卡洛积分方法计算该点的间接光照,而由于该点的&L_i&是追踪的后一个交点的,则递归调用castRay函数。
最终返回直接光照与间接光照之和。
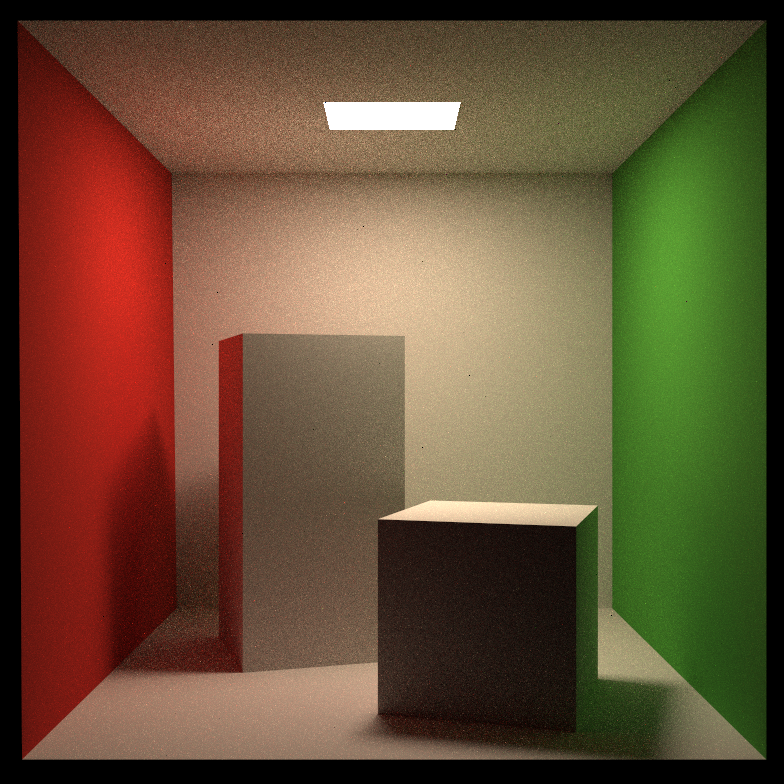
结果
效果图
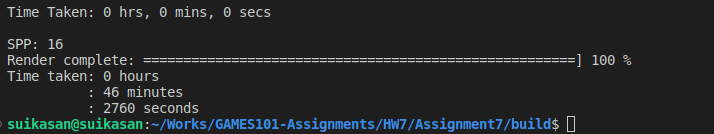
运行时间
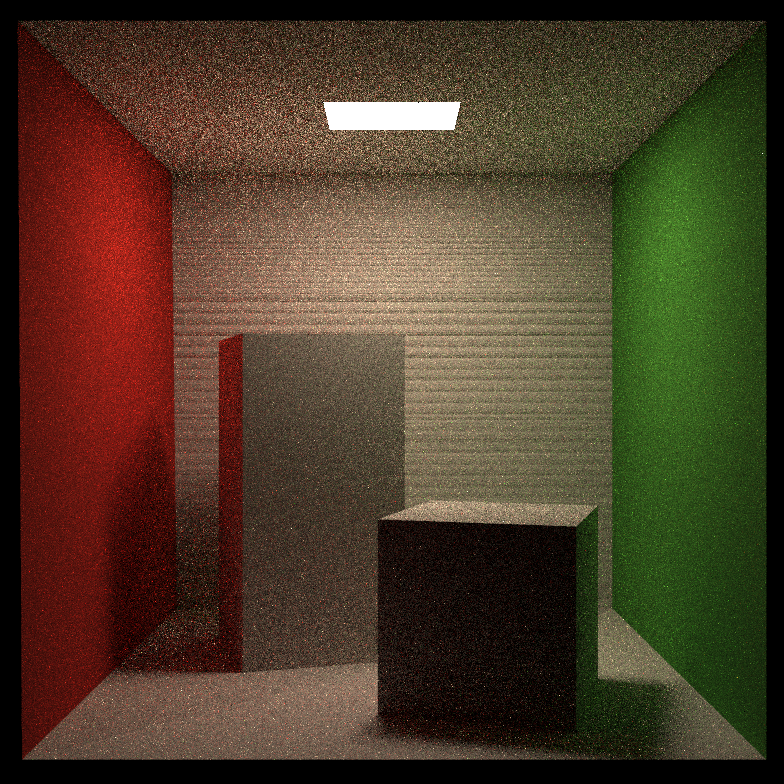
可见渲染结果存在一定问题,存在明显的黑线,而且渲染时间非常长。
问题处理
参考了csdn大佬ycr的账号的文章【GAMES101】作业7 常见问题避坑后,我知道了渲染时间过长的问题很可能是global.hpp下随机数生成函数get_random_float()导致的,而黑线问题很可能是因为直接光部分由于精度问题(EPSILON的取值)导致误判为物体与光源有遮挡。
于是,着手进行修改。
将原随机数生成函数改为如下形式,避免其每次调用时返回同一个值
// in global.hpp
static std::random_device dev;
static std::mt19937 rng(dev());
static std::uniform_real_distribution<float> dist(0.f, 1.f); // distribution in range [1, 6]
inline float get_random_float()
{
return dist(rng);
}将EPSILON改大一些
// in Renderer.cpp
const float EPSILON = 0.001;结果
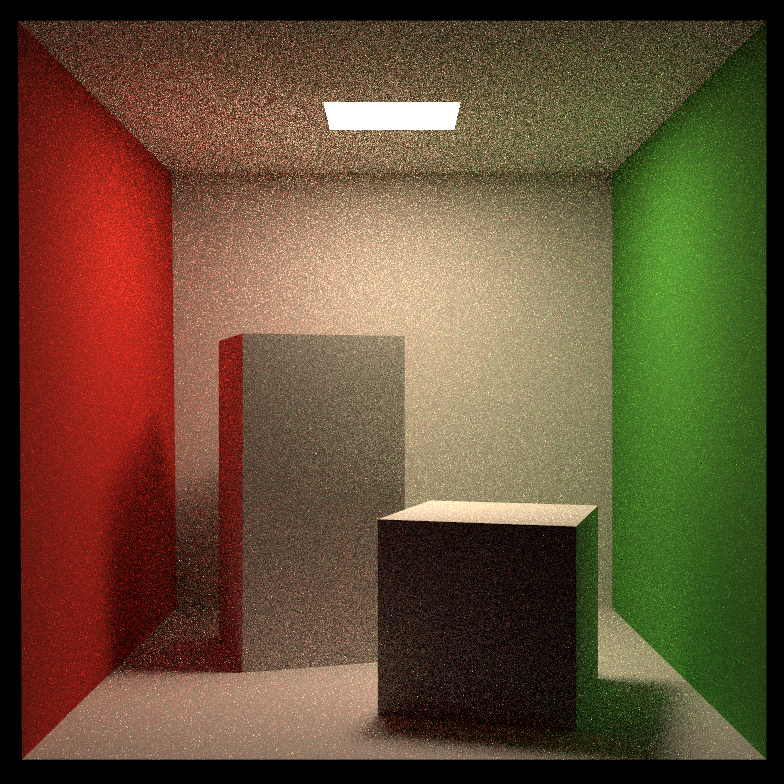

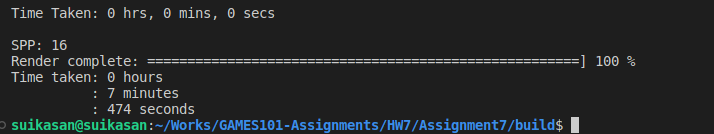
可见渲染时间显著减小,黑线问题也被解决。
多线程
参考文章:【GAMES101】作业7(提高)路径追踪 多线程、Microfacet(全镜面反射)、抗锯齿
在Renderer.cpp中修改
引入头文件
// in Renderer.cpp
#include <omp.h>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>定义para函数作为多线程入口
omp_lock_t lock1;
int prog = 0;
std::mutex lock;
void para(Vector3f eye_pos, std::vector<Vector3f> &framebuffer, const Scene& scene, int spp, float imageAspectRatio, float scale, int start, int end){
int width, height;
width = height = sqrt(spp);
float step = 1.0f / width;
for (uint32_t j = start; j < end; ++j) {
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < scene.width; ++i) {
// generate primary ray direction
for (int k = 0; k < spp; k++){
float x = (2 * (i + step / 2 + step * (k % width)) / (float)scene.width - 1) *
imageAspectRatio * scale;
float y = (1 - 2 * (j + step / 2 + step * (k / height)) / (float)scene.height) * scale;
Vector3f dir = normalize(Vector3f(-x, y, 1));
framebuffer[j * scene.width + i] += scene.castRay(Ray(eye_pos, dir), 0) / spp;
}
}
omp_set_lock(&lock1);
prog++;
UpdateProgress(prog / (float)scene.height);
omp_unset_lock(&lock1);
}
}// in Renderer.cpp
void Renderer::Render(const Scene& scene)
{
std::vector<Vector3f> framebuffer(scene.width * scene.height);
float scale = tan(deg2rad(scene.fov * 0.5));
float imageAspectRatio = scene.width / (float)scene.height;
Vector3f eye_pos(278, 273, -800);
int m = 0;
int thread_num = 32;
int thread_step = scene.height / thread_num;
std::vector<std::thread> rays;
// change the spp value to change sample ammount
int spp = 16;
std::cout << "SPP: " << spp << "\n";
// for (uint32_t j = 0; j < scene.height; ++j) {
// for (uint32_t i = 0; i < scene.width; ++i) {
// // generate primary ray direction
// float x = (2 * (i + 0.5) / (float)scene.width - 1) *
// imageAspectRatio * scale;
// float y = (1 - 2 * (j + 0.5) / (float)scene.height) * scale;
// Vector3f dir = normalize(Vector3f(-x, y, 1));
// for (int k = 0; k < spp; k++){
// framebuffer[m] += scene.castRay(Ray(eye_pos, dir), 0) / spp;
// }
// m++;
// }
// UpdateProgress(j / (float)scene.height);
// }
#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i = 0; i < thread_num; i++)
para(eye_pos, std::ref(framebuffer), std::ref(scene), spp,
imageAspectRatio, scale, i * thread_step, (i + 1) * thread_step);
UpdateProgress(1.f);
// save framebuffer to file
FILE* fp = fopen("binary.ppm", "wb");
(void)fprintf(fp, "P6\n%d %d\n255\n", scene.width, scene.height);
for (auto i = 0; i < scene.height * scene.width; ++i) {
static unsigned char color[3];
color[0] = (unsigned char)(255 * std::pow(clamp(0, 1, framebuffer[i].x), 0.6f));
color[1] = (unsigned char)(255 * std::pow(clamp(0, 1, framebuffer[i].y), 0.6f));
color[2] = (unsigned char)(255 * std::pow(clamp(0, 1, framebuffer[i].z), 0.6f));
fwrite(color, 1, 3, fp);
}
fclose(fp);
}结果
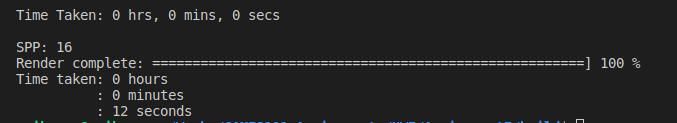
SPP = 16
渲染结果与上面一致
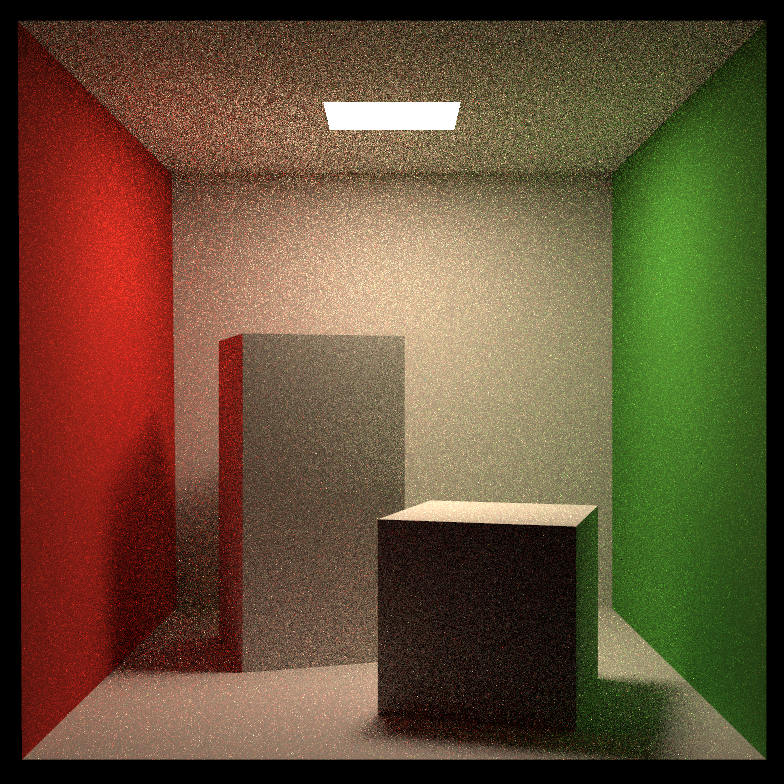

渲染时间显著缩短
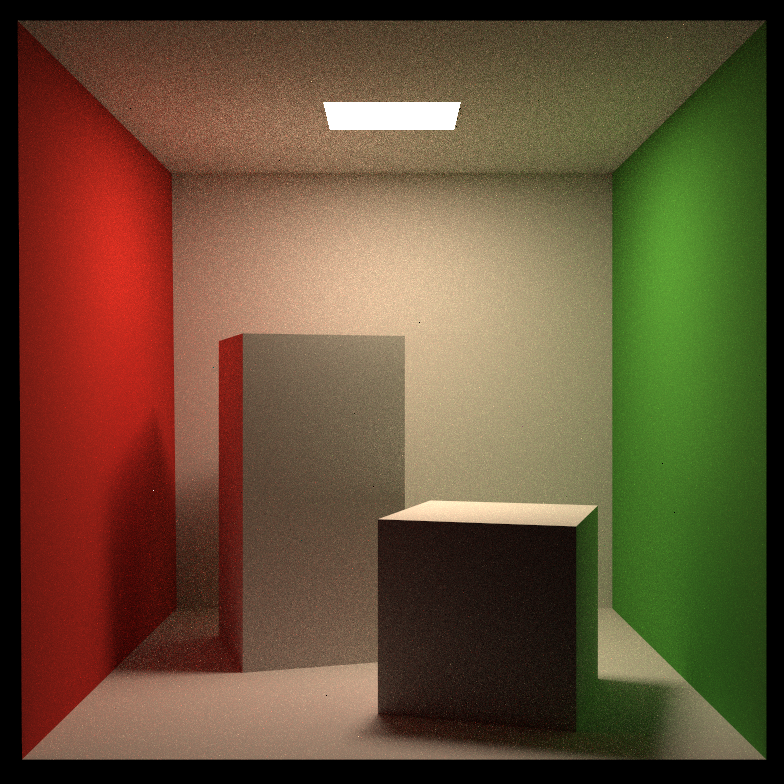
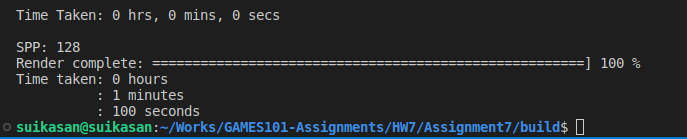
SPP = 128
噪点减少
若要去除白色噪点,需要对castRay函数进行修改,防止pdf过小,作为除数导致最后像素值趋于最大,即白色。因此加上判断pdf > EPSILON
float pdf = interNextP.m->pdf(ray.direction, p2nextpDir, interObj.normal);
if(pdf > EPSILON){
L_indir = castRay(p2nextpRay, depth + 1)
* interObj.m->eval(ray.direction, p2nextpDir, interObj.normal)
* dotProduct(p2nextpDir, interObj.normal) / pdf / RussianRoulette;
}结果
SPP = 128